A Practical Guide to Autonomous Purchase Requisition in Procurement Processes
- Autonomous systems are outcome-driven, adapting in real time to reach the goal, including switching to approved alternative vendors when needed.
- Traditional systems ‘block’ requests with errors, while conversational AI guides them toward compliant choices through practical, in-context suggestions.
- Each decision includes a transparent trail showing which contract, historical price, or compliance policy informed it, reinforcing user trust.
February 17, 2026 | Purchasing 9 minutes read
Most procurement delays begin when a request enters the system. Manual intake and approvals consume time, and incomplete or incorrect requests trigger back-and-forth that compounds the delay.
Autonomous purchase requisition addresses these issues by shifting validation and decision-making to the moment of request creation, before errors travel downstream.
Many organizations struggle with autonomy because it gets treated as basic automation or is evaluated against the wrong capabilities. AI-driven decisioning evaluates requests as they enter, validates them against policy, and routes them appropriately, which reduces friction while maintaining control.
This article explains what autonomous purchase requisition is and how to implement it effectively.
Why Autonomous Purchase Requisition Matters (And Why It’s Been Painful)
A requisition marks the moment intent becomes a commitment, setting expectations for cost, purpose, and approval before any supplier is involved. Everything that follows, from sourcing decisions to purchase orders and invoices, depends on what happens at this entry point.
What is a Purchase Requisition?
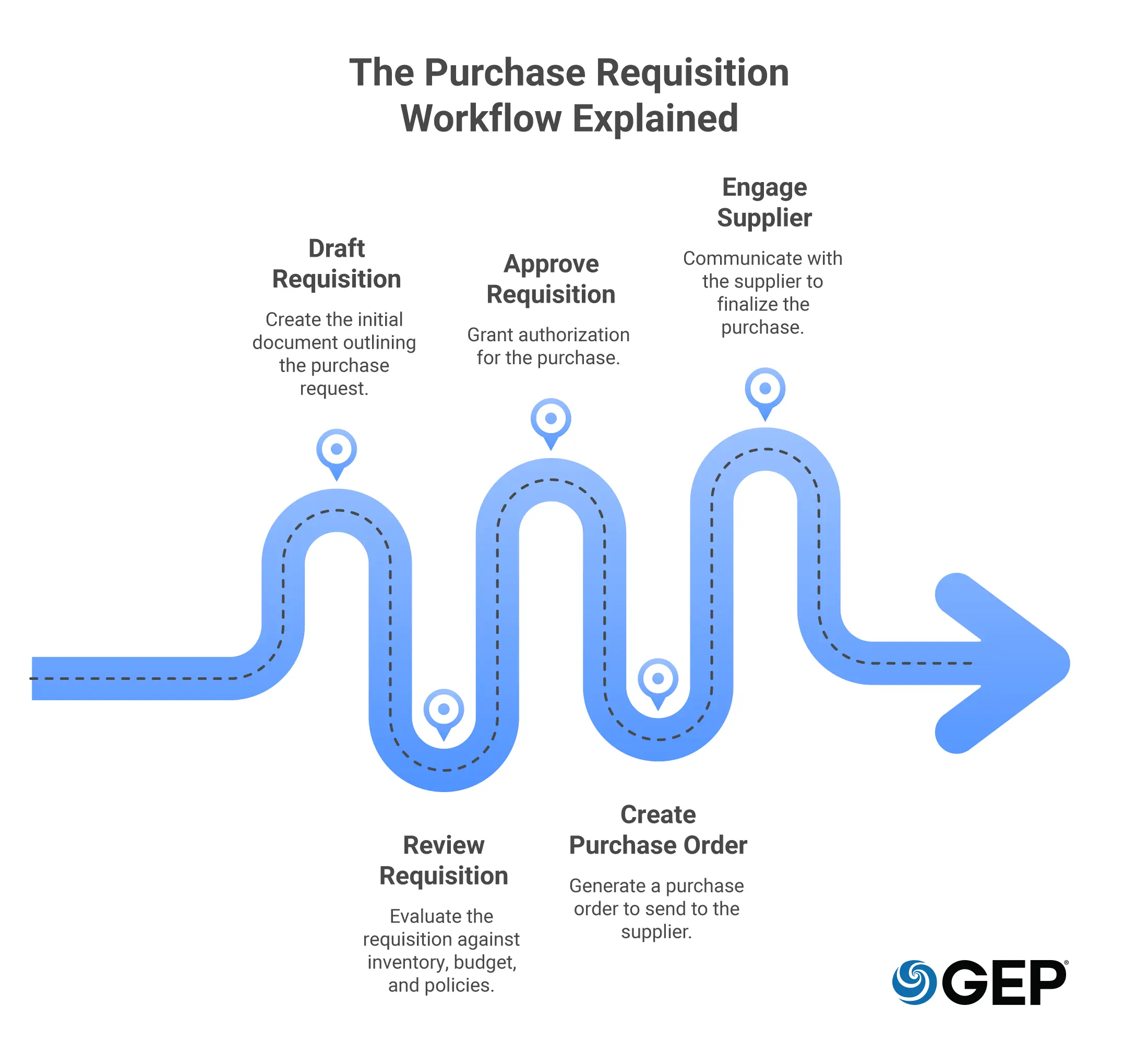
A purchase requisition serves as the internal record that authorizes a purchase. It signals intent, ties the request to budget ownership, and triggers procurement action. For audit and control purposes, it becomes the reference point that teams rely on later.
That record moves through a defined workflow. Each stage reflects a decision state, from early drafting through review and eventual conversion. This structure allows teams to track movement without relying on manual follow-ups.
Before approval, requests are evaluated against available inventory, budget limits, and policy requirements. This prevents overspending and maverick spending right at the start.
Once cleared, the requisition advances to purchase order creation and supplier engagement. What happens at this stage determines how cleanly the rest of the process runs.
The Problem with Traditional Requisition
Traditional requisition processes create friction because they depend on rigid forms and heavy manual input tied to fixed approval paths. Users struggle to choose the right categories or suppliers, leading to incomplete or inaccurate requests.
Those issues surface later in the approval process, where limited context slows decisions and forces procurement teams to step in and correct errors instead of focusing on spend control.
Autonomous purchase requisition resolves these issues by moving away from rigid, rule-driven workflows toward systems designed around outcomes. AI-driven decision-making governs intake and validation as requests enter the system, then directs them forward based on policy and context.
Bring True Autonomy Into Your Procurement Flow
AI supports faster intake with guided, compliant choices
Features or Capabilities to Look for to Automate the Purchase Requisition Process in Procurement
The following capabilities separate true autonomy from surface-level automation:
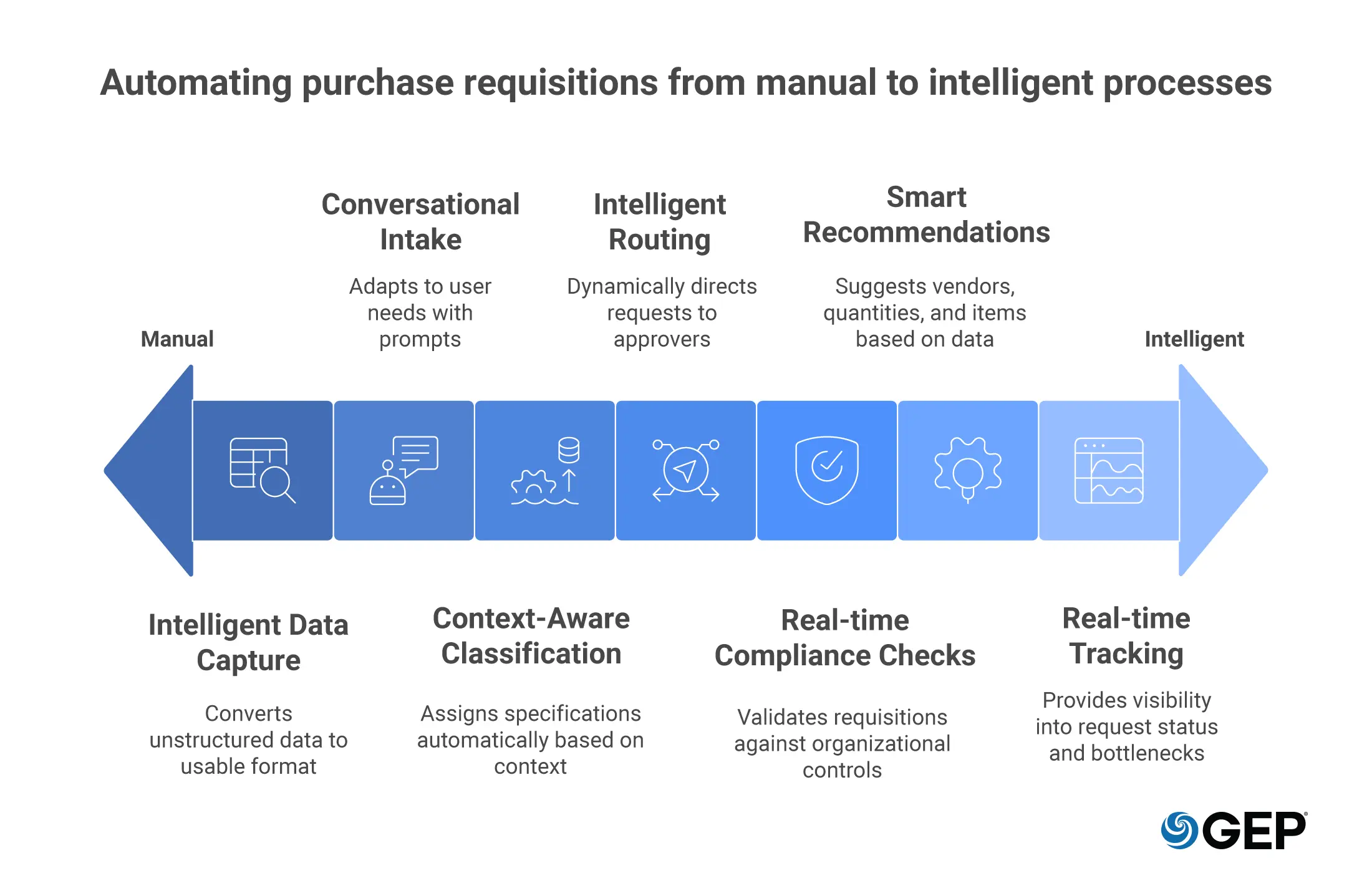
Intelligent Data Capture
Requests often arrive through free text, emails, voice notes, PDFs, or supporting documents. This is unstructured data for any platform to ingest and automatically make sense of. AI interprets these inputs accurately and converts them into usable data at the point of entry into the database. The result is reduced manual effort and the prevention of errors from taking root early.
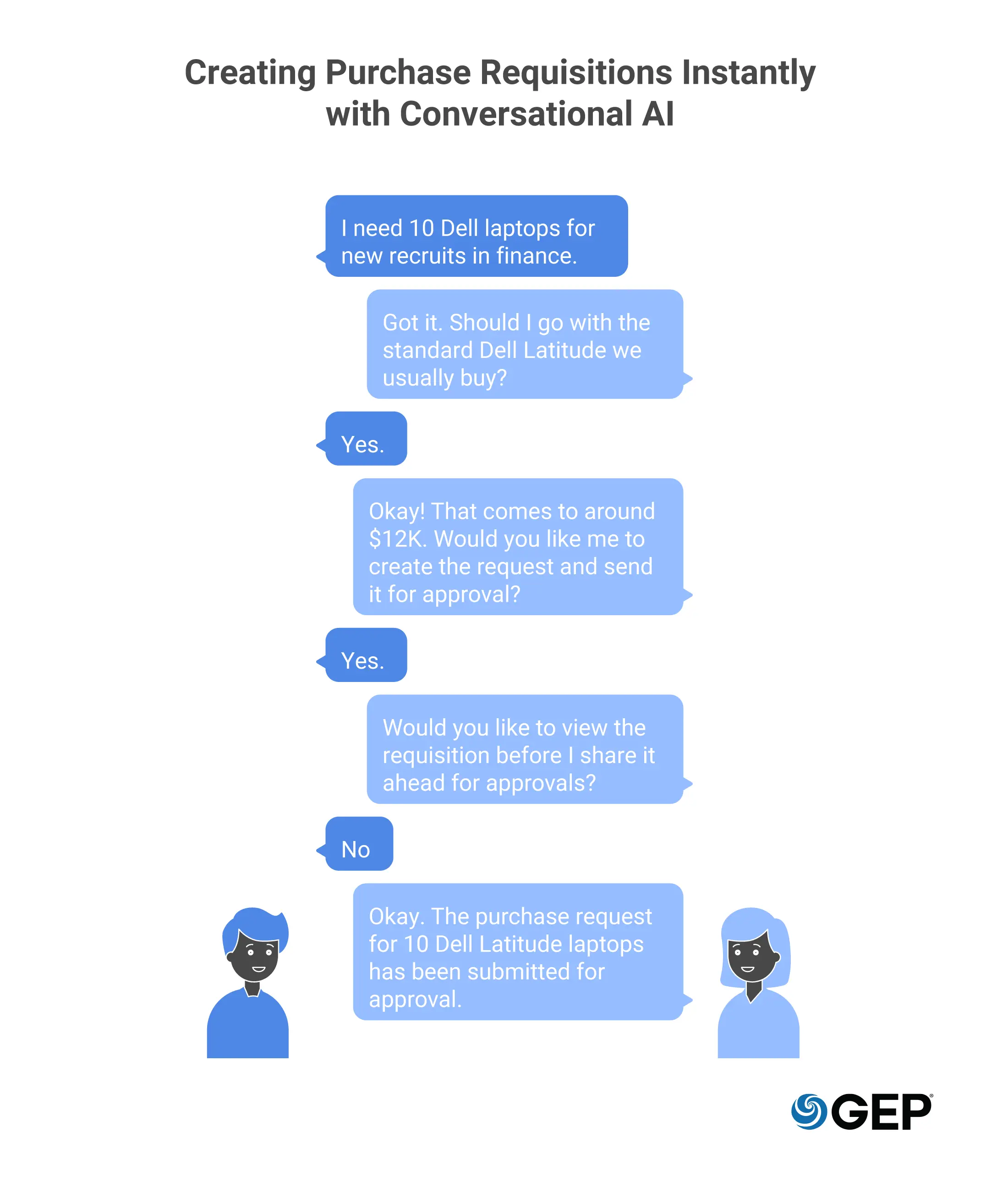
Conversational Intake
AI lets users state what they need in plain language. The system responds with prompts or questions that tighten requirements as the request develops. Adoption improves because the process adapts to users, not the other way around.
Here’s how a chat with a conversational requisition agent would look like:
Context-Aware Classification
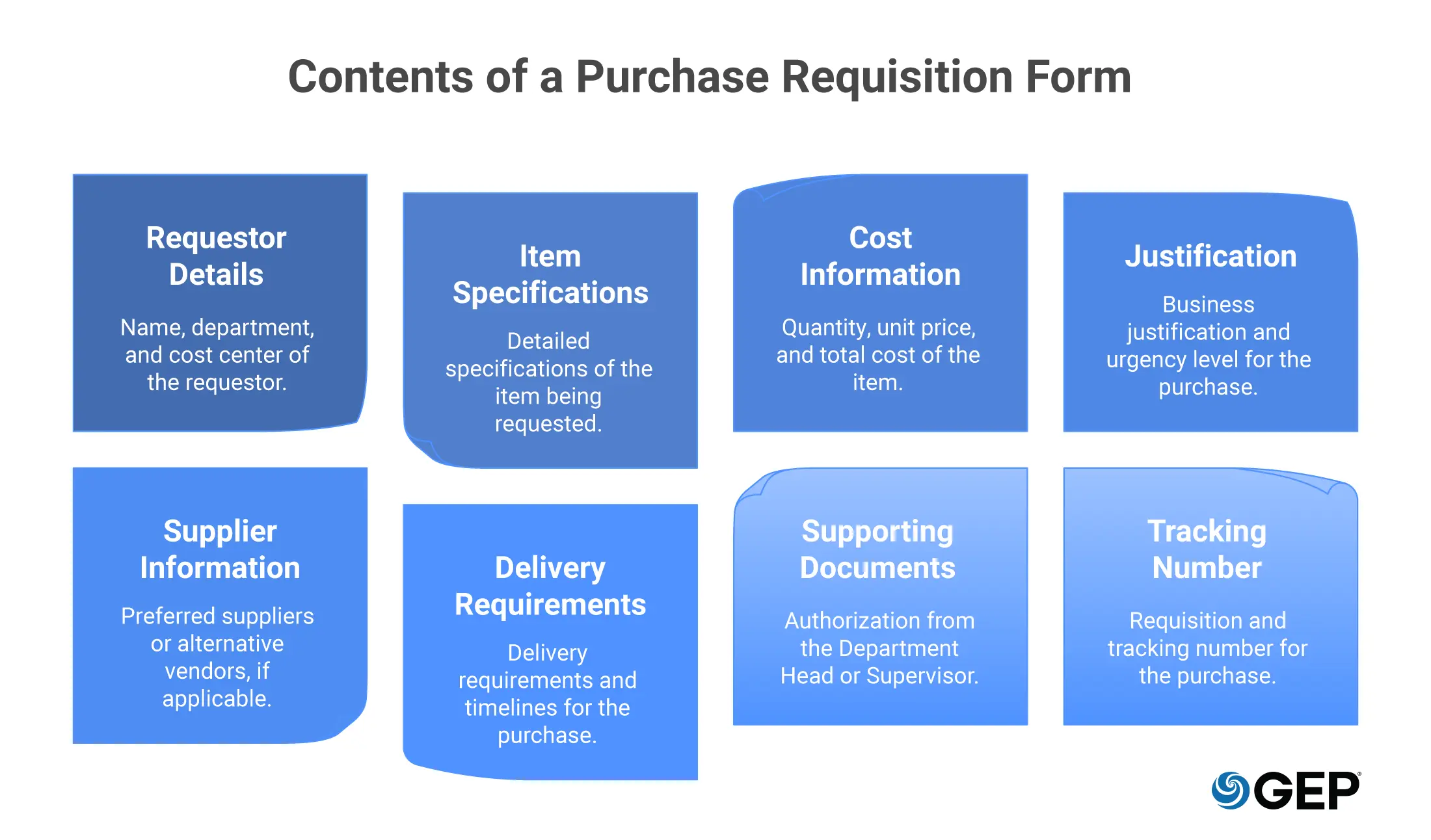
Normally, users must know the right specifications and codes while creating a purchase requisition form. A typical requisition entry includes detailed specifications: item description, exact quantity, unit price or estimate, cost center/GL code, delivery location, required-by date, justification, and approver routing.
Context-aware classification removes that burden by assigning them automatically as requests are created. AI draws on historical patterns and surrounding signals to place each request correctly, which protects sourcing decisions and preserves spend visibility.
Intelligent routing
AI adjusts dynamically, directing each request to the right approver based on context rather than fixed chains. It avoids common hold-ups by dynamically handling exceptions through rerouting or escalation. Smart routing keeps the flow moving without manual intervention.
Real-time compliance checks
AI validates each requisition against the controls your organization has already set, such as rules for budgets, purchasing rules, ESG, and other contractual boundaries. The system flags or blocks any out-of-policy orders automatically.
Smart recommendations
AI learns from prior requisitions and purchasing behavior and applies that insight as new requests enter the system. Using historical data and supplier catalogs, it can recommend preferred vendors, optimal quantities, or alternative items.
It also anticipates which approvals or items are likely required and bases those recommendations on real usage patterns. When constraints apply, the system suggests suppliers that align with existing contracts.
Real-time tracking and reporting
Dashboards show which requests are pending, delayed, or complete, and highlight patterns such as recurring slowdowns within a team. This level of visibility turns procurement into an active pipeline rather than a black box.
When delays surface, managers receive notifications so they can intervene in time. Tracking at this level allows teams to spot and address bottlenecks or compliance issues as they occur, instead of finding them later.
Strengthen Your E&U Supply Chain with Predictive Insights
Forecast material needs, predict asset failures, and plan sourcing with precision
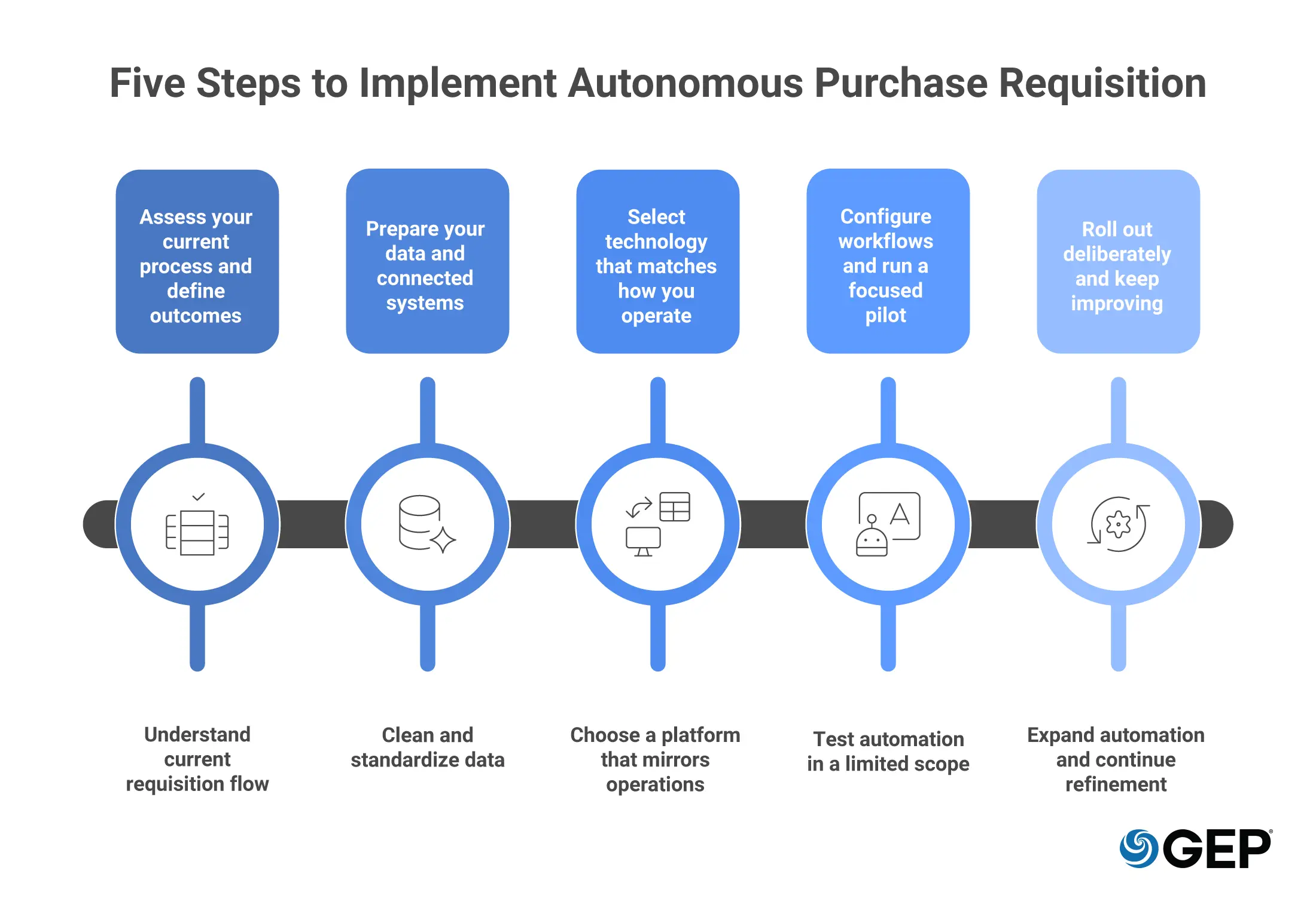
How to Move to Autonomous Purchase Requisition in Five Steps
Autonomous purchase requisition changes how work moves through procurement in practice. Successful implementation depends on sequencing, not speed.
These five steps help you move from fragmented workflows to true autonomy.
1. Assess your current process and define outcomes
Start by understanding how requisitions move through your organization right now, because automation only improves what you can already see clearly.
Look at cycle time alongside how approvals actually flow, note where errors trigger rework, and pay attention to the points where requests slow down or get pushed back. This view gives you a factual baseline, which is essential if you want later improvements to be credible rather than anecdotal.
Once that baseline is clear, define outcomes in terms you can track over time, since improvements only matter when they show up consistently in the data.
Faster cycles or reduced manual effort should tie directly to those measures, which is why the metrics need to be set before automation goes live and usage begins to scale. That way, progress stays visible as behavior changes, not just when results are reported.
This step sets direction. Without it, later decisions lose clarity.
2. Prepare your data and connected systems
Automation reflects the quality of the data behind it. Review item masters, supplier records, and historical requisitions closely. Remove duplicates, update supplier information, and standardize descriptions so the system has reliable inputs to learn from.
Confirm that enterprise resource planning and finance systems can connect without heavy customization.
Many platforms offer connectors, but integrations still require validation. Providing at least a year of historical requisition data improves pattern recognition and reduces manual tuning.
Clean inputs limit rework later and reinforce trust in the system.
3. Select technology that matches how you operate
Technology selection works when it mirrors how requisitions actually move through your organization. The goal is to choose a platform that understands requests as they come in and moves them through approvals using policy logic instead of fixed paths or manual handoffs.
Bring in information technology early to validate security posture and integration effort. Procurement, in parallel, should confirm that policy controls can be configured directly in the system and that budget enforcement happens automatically without side processes.
The right platform aligns with existing decision-making behavior and improves speed and consistency.
4. Configure workflows and run a focused pilot
Once selected, configure approval logic, budget thresholds, and supplier references with care. Avoid wide rollouts at this stage.
Start with a defined scope, such as a single department or spend area, so changes are easier to observe.
During the pilot, watch what actually shifts. Approvals should move with less delay, and exceptions should appear clearly rather than disappearing into queues.
Use this feedback to adjust routing, thresholds, and data mappings before expanding further.
5. Roll out deliberately and keep improving
Expand in phases so teams can adjust without disruption to daily work.
Training should focus on how responsibilities change in practice, including how leaders review and approve requests through the system as well as through conversational interfaces.
Improvement continues after launch. That’s where value compounds.
Overcoming Challenges in Implementing Autonomous Purchase Requisition
Autonomous purchase requisition introduces resistance that must be addressed early to avoid slowing adoption and eroding confidence.
Data quality and readiness
Autonomous requisition depends on clean master data. Inconsistent item and supplier records introduce errors that automation will scale, which is why data must be standardized and validated before deployment.
Prioritize a data cleansing phase. Implement a centralized Master Data Management (MDM) strategy and use AI-powered classification tools to clean and enrich data before the autonomous engine goes live.
System integration complexity
Autonomous requisition depends on ERP integration, which legacy or heavily customized systems often complicate. Integration readiness needs to be confirmed early, including whether native connectors are sufficient or middleware is required.
User adoption and change management
New systems often feel restrictive at the point of use. Adoption improves when creating a requisition feels simpler, and approvers understand where judgment still applies. Resistance fades when decision logic is visible, and intervention points are clear.
Conversational intake and guided flows support this shift. The experience should feel familiar and intuitive, with AI nudging users toward preferred suppliers and pre-negotiated contracts so the compliant path is also the easiest one.
Confidence thresholds help manage the transition to autonomy. High-confidence requests move forward automatically. Lower-confidence requests are flagged for human review, keeping control where it matters.
Complex Non-Catalog Requisitions
Requisitions of standard items like laptops or office supplies are easy to automate. However, complex services or custom-engineered parts require nuanced descriptions that are difficult for basic bots to interpret.
Use Natural Language Processing (NLP) systems to read free-text descriptions or emails, and map them to the correct category codes and supplier capabilities using historical data.
Policy ambiguity or incorrectness
Policy ambiguity limits automation because the system can only enforce rules that are explicit and consistent. In many organizations, that means simplifying or standardizing policies before autonomy can scale responsibly. Clear rules allow decisions to move faster without increasing exception handling.
Start small. Focus on a high-volume, low-complexity category like MRO (Maintenance, Repair, and Operations) or IT peripherals. Prove the ROI before scaling to more complex categories, such as chemicals or energy services. In most cases, cross-functional leadership support is key.
The Road Ahead for Autonomous Requisitions
The future of procurement is increasingly autonomous. Advances in AI and agentic technology mean requisitioning will become more conversational, predictive, and integrated. Autonomous requisitioning will link tightly with predictive analytics, IoT data (e.g. smart stock monitors), and advanced bots that can span the entire source-to-pay cycle.
For any procurement leader ready to transform their requisition process, the first step is to embrace the right technology.
If you want to move faster without losing control, now is the time to rethink how requisitions operate. Autonomous requisition systems allow you to embed intelligence directly into intake, approvals, and execution while maintaining governance. Contact us to begin your journey to autonomous requisitions with modern purchase requisition software delivering the speed, accuracy, and insight your team needs.
FAQs
Autonomous purchase requisition improves accuracy by validating requests at the point of entry instead of after submission. The system checks policy rules, budgets, and contract terms in real time, so incomplete or incorrect requests are corrected before they move into approval. This reduces downstream rework and eliminates many of the errors caused by manual entry.
Autonomy allows procurement to handle higher request volumes without increasing headcount. Intake, routing, and validation are handled continuously by the system, which shifts procurement effort away from transaction management. Scale becomes a function of system capacity rather than human availability.
Success is measured by tracking changes in cycle time, approval speed, exception volume, and user adoption. Strong signals also include improved policy compliance and higher contract utilization. Ongoing analytics show where autonomy is delivering value and where controls may need adjustment.
Autonomous systems can handle catalog-based requests, non-catalog items, blanket requisitions, and service-based purchases. The distinction is not the request type but the level of decision authority assigned to the system. Context-aware rules determine how much autonomy is applied in each case.